A critical vulnerability in Claude Code for Visual Studio Code (VS Code) and other IDE extensions allowed malicious websites to connect to unauthenticated local WebSocket servers, potentially enabling remote command execution. This vulnerability has been fully patched in versions 1.0.24 and later, and all vulnerable versions have been removed from extension stores.
Key points and observations
- On June 23, Anthropic released a security advisory regarding a vulnerability in its IDE extensions for Claude. Anthropic also released a patched version of the extensions.
- This extension is a Model Context Protocol (MCP) server that integrates an IDE (for example, VS Code) with the Claude Code terminal application.
- The vulnerability allowed an attacker to connect to a victim's instance of the Claude IDE MCP server simply due to the victim visiting a website. (Browsers can make connections to WebSocket servers on
localhost.) - The attacker could then execute the commands available in the MCP server, which included reading local files and executing code in Jupyter notebooks within the IDE.
CVE-2025-52882, a significant security flaw in Anthropic's Claude Code extensions for VS Code and other IDEs, has been fully resolved. This vulnerability highlighted a dangerous pattern in development tools where local services lacked proper authentication mechanisms, making them vulnerable to cross-site attacks.
How to know if you are vulnerable
- At this time, Anthropic has pulled all vulnerable versions of the extension from applicable marketplaces.
- The extensions’ configuration in VS Code will force an update, but you are required to restart your extension processes, your IDE, or both.
- If you are running Claude Code and the IDE integration, verify that you are running a patched version.
Vulnerability details
CVE ID: CVE-2025-52882
CVSS Score: 8.8 (High)
Affected Software: Claude Code for VS Code IDE extensions (versions 1.0.23 and earlier)
Advisory: https://github.com/advisories/GHSA-9f65-56v6-gxw7
Resolution Status: FULLY PATCHED
Claude Code extensions established local WebSocket servers to facilitate communication between the IDE integration and the Claude Code terminal application via the MCP. The MCP specifies that servers should use stdio or streaming HTTP, and previously server-side encryption (SSE), for transport. The Claude Code extension also used a WebSocket, bound to localhost, for communication between the MCP server and the IDE.
The vulnerability stemmed from several architectural decisions in pre-patch versions:
- Unauthenticated WebSocket server: The extension started a WebSocket server without implementing any form of client authentication or authorization.
- Browser WebSocket behavior: Unlike traditional HTTP requests, WebSocket connections are not restricted by the browser's same-origin policy.
- Binding to
localhost: The server was bound tolocalhost, but this binding provided no protection against browser-initiated connections from malicious websites. - Dynamic port assignment: The use of dynamic ports provided minimal security through obscurity because port ranges could be systematically attacked with brute force.
The MCP server architecture was designed to enable seamless integration between different Claude Code components. However, the architecture inadvertently created a significant attack surface that was eliminated in the patched version.
Exploitation
For educational purposes, it's worth demonstrating an exploit proof of concept (PoC), if only to highlight the severity of this issue and the ease with which it could be exploited. However, we will not publish the code.
How the exploit works
The exploitation process takes advantage of fundamental characteristics of the WebSocket protocol and browser behavior:
- Initial access: An attacker lures a victim to a malicious website or compromises a legitimate site with malicious JavaScript code.
- Port discovery: The malicious script systematically attempts WebSocket connections to
localhostacross common port ranges. - Connection establishment: When the script discovers the active MCP server port, the script establishes a WebSocket connection.
- Command injection: The attacker sends MCP-formatted commands through the established connection.
The attack is particularly insidious because:
- It requires no user interaction beyond visiting a website.
- Modern browsers display no security warnings for
localhostWebSocket connections. - The attack can be embedded in anything that hosts JavaScript, including advertisements, making it scalable across many victims.
Proof of concept video
We created a video that shows successful exploitation of the extension from a remote host origin.
The demonstration shows:
- Successful WebSocket connection: A malicious website could establish connections to
ws://localhost:42603(or other MCP server ports) by using brute force. - MCP communication: When a connection is established, attackers could send JSON-RPC 2.0 messages that include:
pingcommands to verify server responsivenesstools/listrequests to enumerate available MCP capabilitiestools/callevents to interact with the victim
- File read: Calling tools allows the attacker to read files on the remote system. The PoC demonstrates reading a researcher controlled file, but in a true attack, a malicious actor could read
/etc/passwdor AWS credential files, for example.
Patch analysis
While Anthropic does not make the patch code available easily, you can download the NPM packages to reverse-engineer the patch. Deobfuscation and deminification tools unpack the bundle and allow us to identify changes in the patched version.
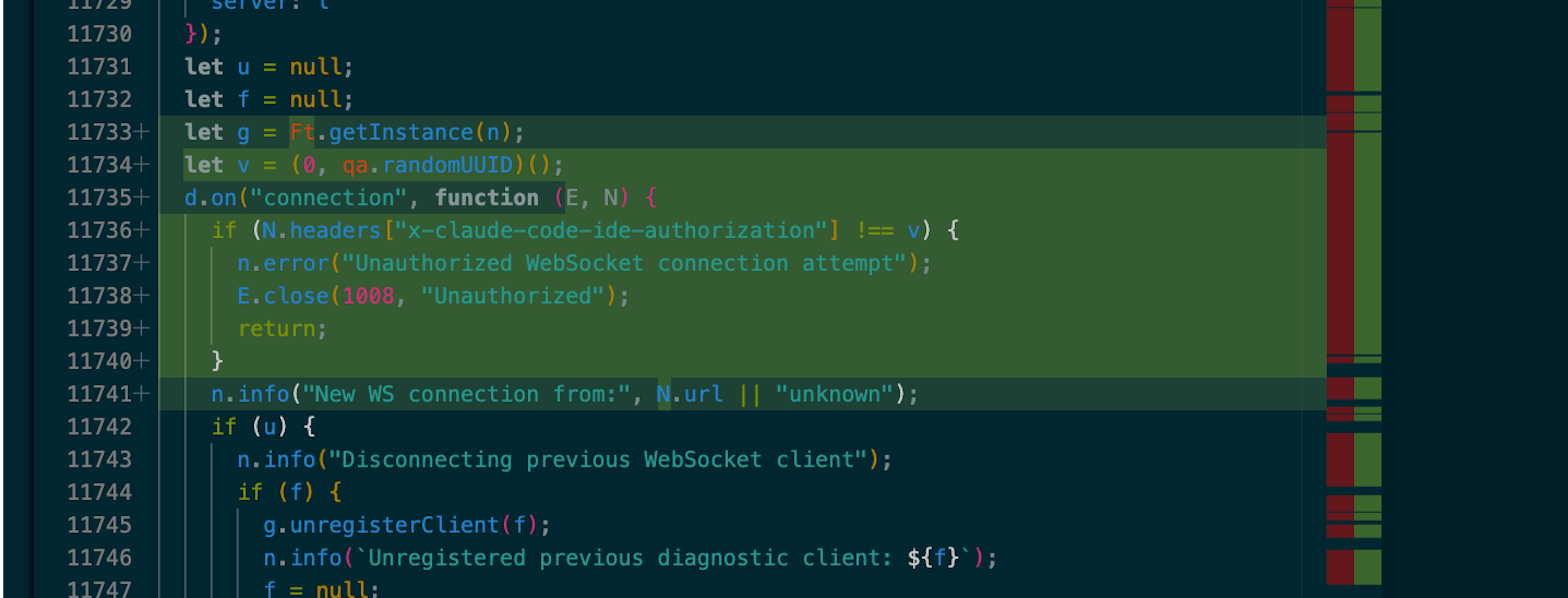
The following diff shows the essential change: The IDE extension will now verify connection attempts by using an auth token. This auth token is stored in a lock file locally and is then provided by the Claude Code CLI as part of its WebSocket connection.

Determining exposure
Take the following steps to determine your exposure to the vulnerability:
- Open VS Code.
- Navigate to Extensions (Ctrl+Shift+X).
- Search for "Claude Code" or check installed extensions.
You were vulnerable if the Claude Code extension version was earlier than 1.0.24 (before June 24, 2025). You are currently protected if the Claude Code extension version is 1.0.24 or later, or if the extension is not installed. This extension is configured to automatically update, but you need to restart your IDE to make the update take effect.
Critical MCP vulnerabilities discovered in 2025
MCP and the AI space in general are rapidly growing, exposing a ballooning attack surface. This MCP vulnerability exists within a larger context and history of vulnerabilities, somewhat akin to the early days of web security. Previous vulnerabilities include CVE-2025-49596, the most severe related vulnerability with a CVSS score of 9.4. CVE-2025-49596 affected Anthropic's MCP Inspector through remote code execution via browser-based exploitation combined with cross-site request forgery (CSRF) attacks. This vulnerability was reported on March 26, 2025, and was patched on June 13, 2025, in version 0.14.1.
Additional significant MCP vulnerabilities include CVE-2025-6514 (mcp-remote RCE, CVSS 9.6), CVE-2025-53110 (directory containment bypass, CVSS 7.3), and CVE-2025-53109 (symbolic link bypass, CVSS 8.4). The NeighborJack vulnerability affects MCP servers that are exposed to local network attacks due to binding to 0.0.0.0.
Systemic security challenges in AI development tools
Security researchers have identified broader issues in AI development tools. These issues include prompt injection vulnerabilities in MCP servers, context poisoning attacks, insufficient authentication mechanisms, and input validation problems that lead to SQL injection and command injection vulnerabilities.
VS Code extension security presents ongoing challenges with over 45,000 downloads of malicious extensions detected, typosquatting attacks that target popular extensions, and insufficient security controls in the VS Code Marketplace. Historical vulnerabilities in extensions like GitLens (CVE-2023-46944) demonstrate persistent security weaknesses.
References
- CVE-2025-52882 - NIST National Vulnerability Database
- CWE-1385: Missing Origin Validation in WebSockets
- Anthropic Claude Code Security Documentation
- Testing for WebSockets security vulnerabilities - PortSwigger
- WebSocket Security: Top Vulnerabilities and Mitigations
- Visual Studio Code Extension Security Deep Dive - Snyk Research
- Model Context Protocol (MCP) Specification




